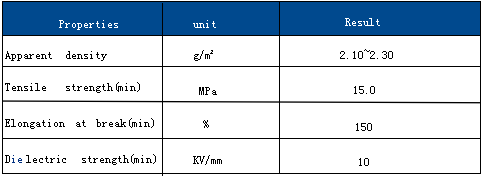
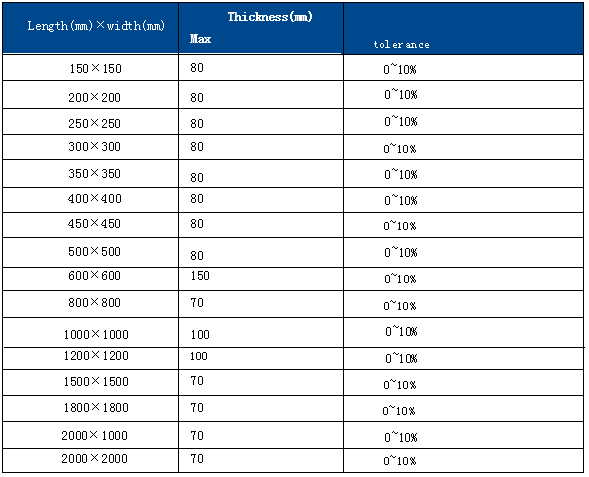
Introduction to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Sheets
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Sheets, also known as PTFE Plates in English, are sheet or plate materials made from PTFE resin through compression molding or hydraulic forming, followed by high-temperature sintering. As one of the most fundamental and common forms of PTFE products, they are widely used in industries as critical non-metallic materials due to their exceptional comprehensive properties.
The name directly highlights its core information:
· Material: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as "Teflon" or the "King of Plastics."
· Form: Sheet/Plate, typically distinguished by thickness—thin ones are called sheets, while thick ones are called plates.
Key Characteristics
PTFE sheets perfectly inherit almost all the excellent properties of PTFE resin:
1. Exceptional Chemical Stability (Core Advantage): Resists almost all strong acids, strong alkalis, strong oxidizers, and organic solvents, including aqua regia. This is the primary reason for its irreplaceability in harsh chemical environments.
2. Excellent High and Low-Temperature Resistance: Can be used continuously within a temperature range of -180°C to +250°C without significant changes in mechanical properties.
3. Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction: One of the lowest among solid materials (approximately 0.04), offering excellent lubrication, outstanding non-stick, and anti-adhesion properties.
4. Superior Electrical Insulation: Unaffected by environment and frequency, making it an ideal high-frequency insulating material.
5. Non-flammability: Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) above 95, non-combustible, and self-extinguishing.
6. Physiological Inertness: Non-toxic, compliant with FDA standards, and suitable for food and medical industries.
Common Manufacturing Processes and Types
Based on production processes and subsequent machining, PTFE sheets are mainly categorized as follows:
· Molded Sheet:
· Process: PTFE suspension resin powder is filled into a mold of specific dimensions, compressed under pressure to form a billet, sintered in a high-temperature furnace, and finally cooled to set the shape.
· Characteristics: This is the most commonly used process. The sheets are dense with uniform properties and can be produced in various thicknesses and sizes. The surface is non-smooth and retains the resin's natural color (white).
· Skived Sheet:
· Process: Large cylindrical billets (blanks) are first made through compression molding and sintering, then thinly sliced (skived) on a precision lathe to produce thin sheets.
· Characteristics: Primarily used for producing very thin sheets (typically 0.1mm - 2mm). The surface is smooth with high dimensional accuracy and uniform texture. Ideal for manufacturing gaskets and seals.
· Oriented Film/Sheet:
· Process: Thin sheets obtained by skiving are biaxially stretched to align the PTFE molecular chains.
· Characteristics: Features a microporous structure with significantly improved mechanical strength but also some breathability. Commonly used in medical and environmental protection fields.
· Filled PTFE Sheet:
· Process: PTFE resin is mixed with various fillers (such as glass fiber, graphite, carbon fiber, bronze, molybdenum disulfide, etc.) and then compression-molded and sintered.
· Characteristics: Aims to address the shortcomings of pure PTFE. Greatly improves wear resistance, compressive strength, stiffness, and creep resistance while retaining good chemical resistance. Suitable for wear-resistant applications.
Main Application Areas
The unique properties of PTFE sheets make them the material of choice in numerous industrial fields:
· Chemical Industry:
· Sealing Gaskets: Used to make corrosion-resistant sealing gaskets for towers, tanks, reactors, and pipeline flanges.
· Lining Material: Serves as a lining for reaction kettles, storage tanks, and vessels to prevent corrosion of the shell.
· Scraper Plates/Baffles: Used in components exposed to corrosive media.
· Mechanical Engineering:
· Wear Plates/Guides: Used in machine tools, food machinery, and other applications requiring low friction and non-stick properties.
· Oil-Free Lubrication Materials: Used to make self-lubricating components such as bearings, piston rings, and guide pads.
· Insulating Components: Used as insulating gaskets and barriers in electrical equipment.
· Food and Pharmaceutical Industries:
· Used for non-stick linings and conveyor belts in food drying equipment and pharmaceutical production machinery.
· Electronics and Electrical Industry:
· Used in insulating components for high-frequency communication equipment, microwave ovens, and other fields.
Comparison with Other Engineering Plastic Sheets
| Property |
PTFE Sheet |
UHMW-PE Sheet |
PP Sheet |
PVC Sheet |
| Chemical Stability |
Excellent |
Good |
Fair |
Good (acid-resistant) |
| v |
-180°C ~ +250°C |
-100°C ~ +80°C |
0°C ~ +90°C |
-10°C ~ +60°C |
| Coefficient of Friction |
Very Low (0.04) |
Low (0.10) |
Medium |
Medium |
| Non-stick Properties |
Excellent |
Good |
Fair |
Fair |
| Mechanical Strength |
Low |
Very High |
Medium |
Medium |
| Cost |
High |
Medium |
Low |
Low |
| Primary Advantage |
Ultimate corrosion resistance, ultra-wide temp range, non-stick |
Wear resistance, impact resistance |
Low cost, lightweight |
Low cost, easy processing |
|
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Sheets are high-performance fundamental engineering materials with exceptional chemical inertness, an ultra-wide operating temperature range, and an extremely low coefficient of friction as their core value.
· Core Value: They are irreplaceable solutions in highly corrosive, high-low temperature alternating, non-stick, or insulating extreme conditions where metals or other plastic sheets cannot perform. They are typically not used as structural load-bearing components but as functional materials for sealing, lining, wear resistance, and insulation.
· Key Selection Factor: The appropriate type must be selected based on specific applications:
· For pure corrosion resistance and insulation, choose molded sheets.
· For thin gaskets and seals, choose skived sheets.
· For wear-resistant, pressure-bearing, and anti-creep applications, filled PTFE sheets are essential.