
Productscpzx




Features:
There are three kinds of PTFE rods to offer. One is manufactured by paste extruding method in the diameter from 2 to 4mm and the other is made by ram extruding method in the diameter from 5 to 200mm;rods over the diameter 55 to 300mm are manufactured by moulding.
PTFE is the most chemical resistant and the best dielectric of all known plastics .lIt is not aging and binding.It can be used from-180 ℃~260 ℃ under on burthen circumstances.PTFE has the lowest coefficient of friction of all known solid materials.
Applications:
Electrical insulation,seal,antisticking materials.
Main properties:
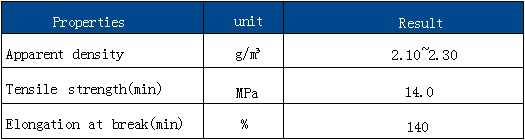
Specifications:
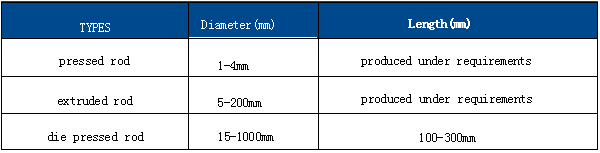
Introduction to Molded Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Rods
Molded Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Rods are rod-shaped materials made from PTFE resin through a compression molding process. This is a semi-finished product that typically requires subsequent machining (such as turning or cutting) to become a final part.
The name directly highlights three key pieces of information:
- Material: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as "Teflon" or the "King of Plastics."
- Process: Compression Molding, the initial forming method.
- Form: Rod.
Manufacturing Process: Compression Molding
"Compression molding" is the core process for manufacturing these rods. The general steps are as follows:
1. Feeding: A certain amount of fine white powdered PTFE resin is filled into a pre-designed metal mold cavity.
2. Pre-pressing: Preliminary pressure is applied to the powder in the mold at room temperature to form a relatively compact preform (commonly called a "blank" or "billet").
3. Sintering: The mold with the billet is placed in a high-temperature sintering furnace and heated above the melting point of PTFE (typically between 365°C and 380°C). During this process, the PTFE particles melt and coalesce into a continuous, dense whole.
4. Cooling: The material is slowly cooled to room temperature to allow crystallization and setting.
5. Demolding: The formed PTFE rod is removed from the mold.
Rods produced through this process are available in various diameters and lengths to meet different requirements.
Key Characteristics
Molded PTFE rods inherit almost all the excellent properties of pure PTFE:
1. Outstanding Chemical Stability: Resists almost all strong acids, strong alkalis, strong oxidizers, and organic solvents, including aqua regia. This is its most famous property.
2. Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction: One of the lowest among solid materials, offering excellent lubricity and non-stick properties.
3. Wide Operating Temperature Range: Can be used continuously within a temperature range of -180°C to +250°C without significant degradation in performance.
4. Excellent Electrical Insulation: Unaffected by environment and frequency, making it an ideal high-frequency insulating material.
5. Non-stick and Hydrophobic Properties: Almost no substances adhere to its surface, and it repels water.
6. Aging Resistance: Its properties remain unchanged even after long-term exposure outdoors.
Main Application Areas
Molded PTFE rods are semi-finished products. After machining, the parts made from them are widely used in:
- Chemical Industry: Used to manufacture sealing packings, gaskets, valve discs, bearings, linings, and pipeline components to resist corrosive media.
- Electronics and Electrical Industry: Processed into insulating sleeves, sockets, coil bobbins, and chip trays, leveraging its excellent insulation and high-temperature resistance.
- Mechanical Industry: Used to manufacture oil-free lubricated bearings, piston rings, and guide rail gaskets, especially in industries like food and pharmaceuticals where lubricant contamination is not allowed.
- Non-stick Applications: Used in rollers, iron soleplates, and mold release plates where non-stick properties are required.
- Medical and Food Industries: Due to its physiological inertness and compliance with hygiene standards, it is used in medical device components and parts for food processing equipment.
Comparison with Other PTFE Rod Processes
In addition to compression molding, PTFE rods can also be produced through push extrusion. The differences between the two are as follows:
| Property | Molded Rod | Extruded Rod |
| Production Process | Formed by pressing in a mold, then sintered | Pre-pressed into a billet, then continuously extruded under pressure through an extruder and sintered |
| Product Dimensions | Typically larger diameters (up to several hundred mm), limited length | Typically smaller diameters (a few mm to over 100 mm), can be very long (continuous) |
| Structural Density | Very dense and uniform, isotropic (consistent properties in all directions) | May have minor pores, slightly anisotropic (slight differences in radial and axial properties) |
| Surface Appearance | Smooth surface | May have slight longitudinal streaks (extrusion marks) |
| Applications | Suitable for large diameters and high-performance requirements, especially for machining seals | Suitable for long-length, small-diameter rods, generally lower cost |
Molded Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Rods are high-performance engineering plastic semi-finished products manufactured through compression molding and sintering processes.
- Core Value: They perfectly inherit PTFE's top-tier chemical inertness, low friction, wide temperature range, and insulation properties. Due to the characteristics of the molding process, they also offer high density and isotropy.
- Typical Uses: They are ideal blanks for machining various corrosion-resistant, high-temperature-resistant, insulating, and oil-free lubrication parts. Especially in applications requiring large diameters and high material consistency (such as high-performance sealing rings), molded rods are the preferred material.